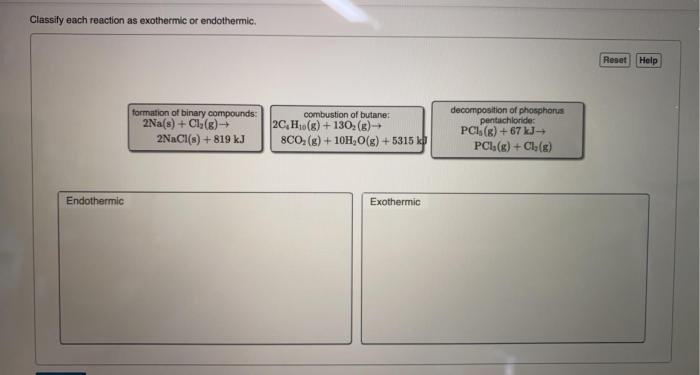
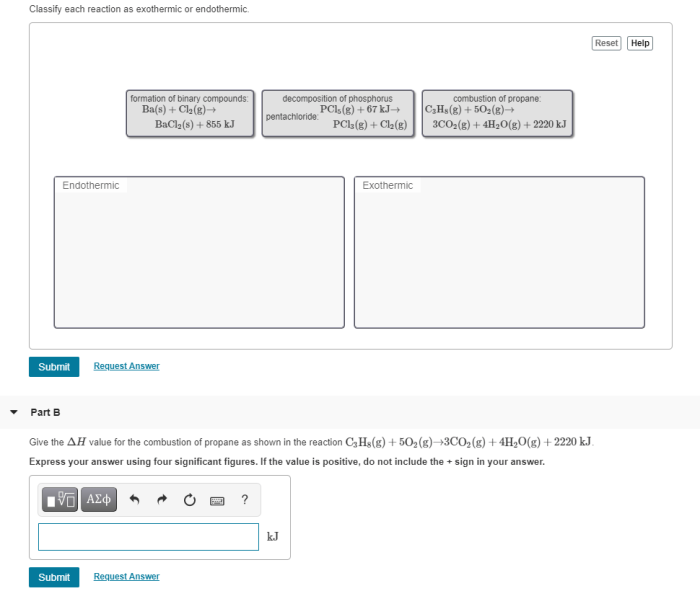
Classify each reaction as exothermic or endothermic delves into the captivating realm of chemical reactions, unraveling the intricate dance between energy and matter. As we embark on this journey, we will explore the fundamental concepts of exothermic and endothermic reactions, unlocking the secrets that govern their behavior.
Throughout history, scientists have sought to understand the nature of chemical reactions, meticulously observing and categorizing them based on their energy exchange with the surroundings. This quest for knowledge has led to the development of sophisticated techniques and the formulation of insightful theories, providing us with a comprehensive framework for classifying reactions as either exothermic or endothermic.
Introduction
Chemical reactions can be classified into two main types: exothermic and endothermic. Exothermic reactions release energy in the form of heat, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings.
The difference between these two types of reactions lies in the change in enthalpy (ΔH) that occurs during the reaction. In exothermic reactions, ΔH is negative, indicating that energy is released. In endothermic reactions, ΔH is positive, indicating that energy is absorbed.
Methods for Classifying Reactions
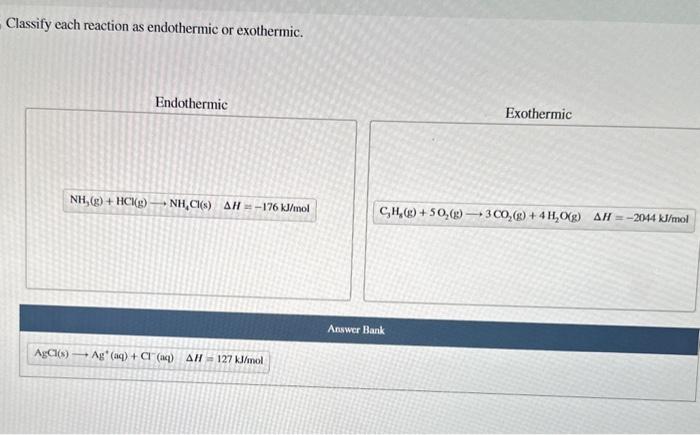
There are several methods that can be used to classify reactions as exothermic or endothermic.
Calorimetry
Calorimetry is a technique that measures the heat released or absorbed during a reaction. A calorimeter is a device that is used to measure the change in temperature of a reaction mixture. The heat released or absorbed by the reaction is then calculated using the following equation:
ΔH = -Q/n
where:
- ΔH is the change in enthalpy (in kJ/mol)
- Q is the heat released or absorbed (in kJ)
- n is the number of moles of reactants
Enthalpy Changes
The enthalpy change of a reaction can also be calculated using the following equation:
ΔH = ΣΔH products– ΣΔH reactants
where:
- ΔH is the change in enthalpy (in kJ/mol)
- ΔH productsis the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the products (in kJ/mol)
- ΔH reactantsis the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the reactants (in kJ/mol)
Heat of Reaction
The heat of reaction is the amount of heat released or absorbed during a reaction. The heat of reaction can be positive or negative, depending on whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
Examples of Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy in the form of heat. Some common examples of exothermic reactions include:
Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions are reactions that involve the burning of a fuel with oxygen. These reactions are highly exothermic, and they release a large amount of heat. Examples of combustion reactions include the burning of wood, gasoline, and natural gas.
Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization reactions are reactions that occur between an acid and a base. These reactions are exothermic, and they release a small amount of heat. Examples of neutralization reactions include the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions are reactions that occur when two solutions are mixed and a solid precipitate forms. These reactions are exothermic, and they release a small amount of heat. Examples of precipitation reactions include the reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions
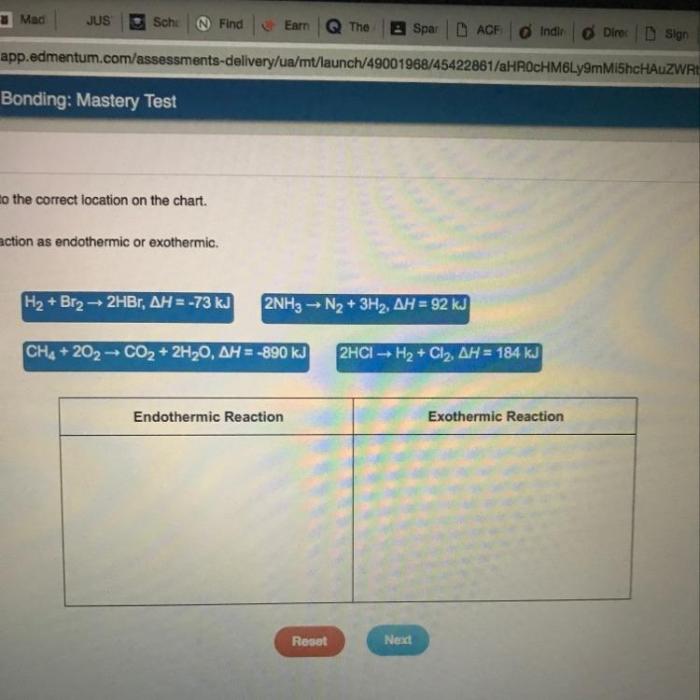
Endothermic reactions are reactions that absorb energy from their surroundings. Some common examples of endothermic reactions include:
Melting
Melting is the process of changing a solid into a liquid. This process is endothermic, and it absorbs energy from the surroundings. Examples of melting include the melting of ice and the melting of metals.
Boiling
Boiling is the process of changing a liquid into a gas. This process is endothermic, and it absorbs energy from the surroundings. Examples of boiling include the boiling of water and the boiling of alcohol.
Dissolving
Dissolving is the process of mixing a solid into a liquid to form a solution. This process is endothermic, and it absorbs energy from the surroundings. Examples of dissolving include the dissolving of salt in water and the dissolving of sugar in water.
Applications of Classifying Reactions
Classifying reactions as exothermic or endothermic has a number of applications. These applications include:
Predicting the Direction of Reactions
The direction of a reaction can be predicted based on its enthalpy change. Exothermic reactions are more likely to occur spontaneously than endothermic reactions. This is because exothermic reactions release energy, which can be used to drive the reaction forward.
Designing Chemical Processes, Classify each reaction as exothermic or endothermic
The enthalpy change of a reaction can be used to design chemical processes. For example, exothermic reactions can be used to generate heat, while endothermic reactions can be used to cool a system.
Understanding the Behavior of Materials
The enthalpy change of a reaction can be used to understand the behavior of materials. For example, the enthalpy change of a melting reaction can be used to determine the melting point of a material.
Expert Answers: Classify Each Reaction As Exothermic Or Endothermic
What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions release energy into the surroundings, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings.
How can I determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic?
One way to determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic is to measure the temperature change of the surroundings during the reaction. If the temperature increases, the reaction is exothermic; if the temperature decreases, the reaction is endothermic.
What are some examples of exothermic reactions?
Some examples of exothermic reactions include combustion reactions, neutralization reactions, and precipitation reactions.
What are some examples of endothermic reactions?
Some examples of endothermic reactions include melting, boiling, and dissolving.