Which statement is correct regarding graded potentials? Graded potentials are a type of electrical signal that can vary in amplitude and duration, unlike action potentials, which are all-or-none signals. Graded potentials are generated by the opening and closing of ion channels in the cell membrane, and they can propagate over long distances without losing their strength.
They play a vital role in many physiological processes, such as sensory transduction, synaptic plasticity, and muscle contraction.
In this article, we will discuss the fundamental differences between graded potentials and action potentials, the process of graded potential propagation, the integration of graded potentials, and the comparison of graded potentials in different cell types. We will also explore the clinical significance of graded potentials and provide examples of their role in various physiological systems.
Graded Potentials vs. Action Potentials
Graded potentials are continuous changes in membrane potential that vary in amplitude and duration, whereas action potentials are brief, all-or-nothing electrical impulses that propagate along the membrane of excitable cells. Graded potentials are caused by the opening and closing of ion channels, which allow ions to flow across the membrane and change the membrane potential.
Action potentials, on the other hand, are caused by the rapid opening and closing of voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels, which create a regenerative cycle that leads to a rapid depolarization and repolarization of the membrane.
Propagation of Graded Potentials
Graded potentials propagate along the membrane by a process called electrotonic conduction. Electrotonic conduction is a passive process that does not require energy and is subject to the properties of the membrane, such as its capacitance and resistance. The amplitude of a graded potential decreases with distance from the site of origin due to the leakage of ions across the membrane and the resistance of the membrane to current flow.
The duration of a graded potential is also affected by the membrane properties, as well as the time course of the opening and closing of ion channels.
Examples of Graded Potentials, Which statement is correct regarding graded potentials
- Receptor potentials in sensory neurons
- Postsynaptic potentials in neurons
- Slow waves in smooth muscle
Integration of Graded Potentials
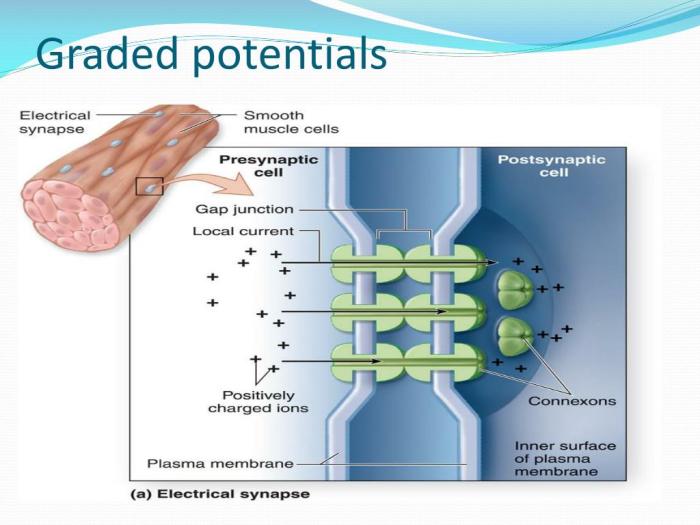
Graded potentials can be integrated in space and time to determine the firing of an action potential. Spatial summation occurs when graded potentials from multiple sources summate at the same time, while temporal summation occurs when graded potentials from the same source summate over time.
Dendrites play an important role in integrating graded potentials, as they allow for the summation of inputs from multiple sources.
Comparison of Graded Potentials in Different Cell Types
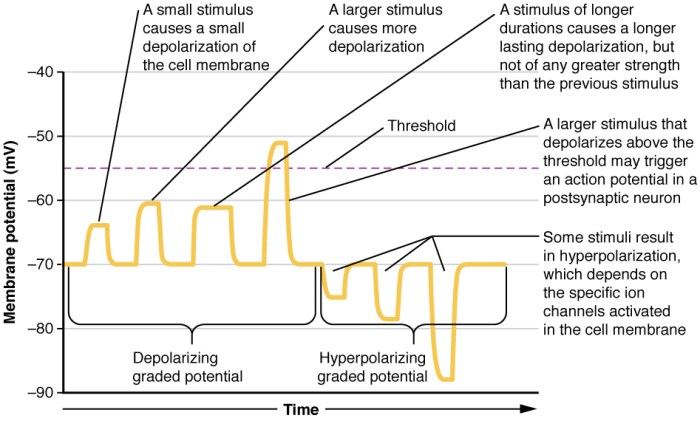
Graded potentials vary in their characteristics in different cell types. In neurons, graded potentials are typically small and short-lived, while in muscle cells, they are larger and longer-lasting. In other excitable cells, such as cardiac cells, graded potentials can have unique properties that contribute to the unique functions of these cells.
Clinical Significance of Graded Potentials
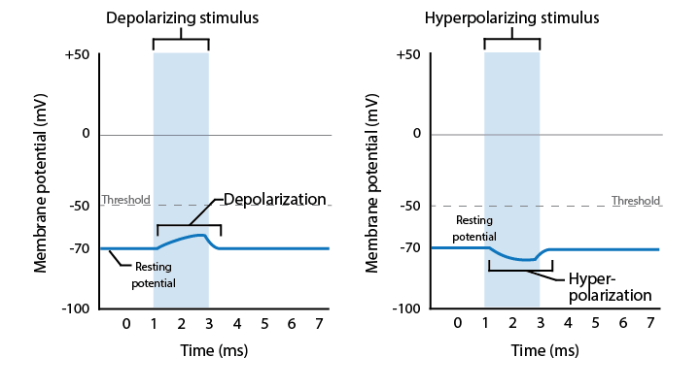
Graded potentials play an important role in sensory transduction and synaptic plasticity. Alterations in graded potentials can contribute to neurological disorders, such as epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Therapeutic interventions that target graded potentials are being developed to treat these disorders.
FAQ Corner: Which Statement Is Correct Regarding Graded Potentials
What is the difference between graded potentials and action potentials?
Graded potentials are electrical signals that can vary in amplitude and duration, while action potentials are all-or-none signals.
How are graded potentials generated?
Graded potentials are generated by the opening and closing of ion channels in the cell membrane.
How do graded potentials propagate?
Graded potentials propagate over long distances without losing their strength.
What is the role of graded potentials in sensory transduction?
Graded potentials play a vital role in sensory transduction, which is the process of converting sensory stimuli into electrical signals.