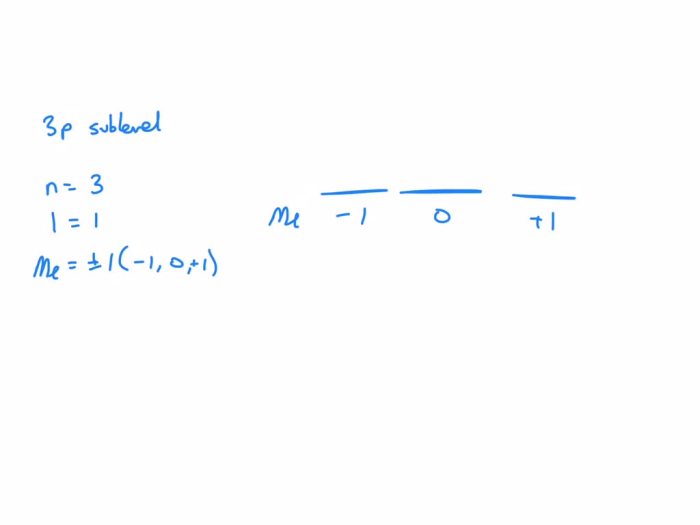Identify the correct values for a 3p sublevel. – Identifying the correct values for a 3p sublevel is a crucial aspect of understanding atomic structure and its implications in chemistry. This concept involves determining the specific quantum numbers that characterize the 3p sublevel, providing insights into its properties, shapes, and energy levels.
The 3p sublevel plays a significant role in various chemical phenomena, including bonding and molecular interactions. By exploring the rules and principles governing the identification of its correct values, we gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of electrons within atoms and molecules.
Overview of 3p Sublevel
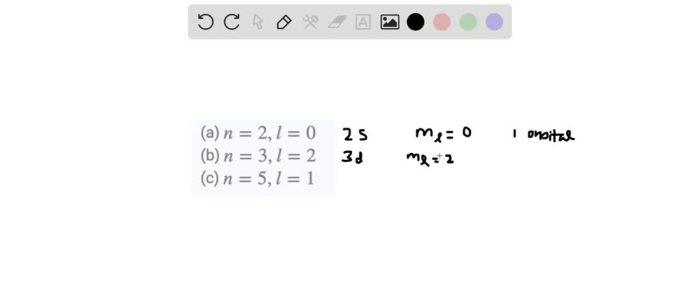
The 3p sublevel is a set of atomic orbitals in the third energy level (n = 3) with an azimuthal quantum number (l) of 1. It consists of three orbitals, each with a different magnetic quantum number (ml): ml = -1, 0, and +1. These orbitals are designated as 3px, 3py, and 3pz, respectively.
The 3p orbitals have a dumbbell shape with a nodal plane at the nucleus. The 3px and 3py orbitals are oriented along the x and y axes, respectively, while the 3pz orbital is oriented along the z axis.
Identifying Correct Values: Identify The Correct Values For A 3p Sublevel.
The correct values for a 3p sublevel can be determined using the following rules:
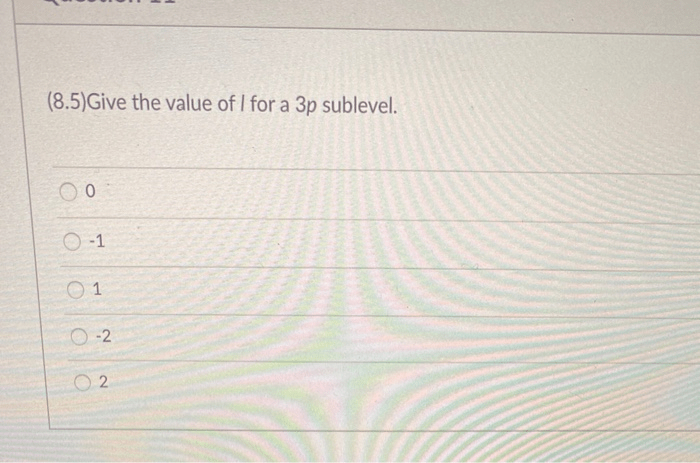
- The principal quantum number (n) must be 3.
- The azimuthal quantum number (l) must be 1.
- The magnetic quantum number (ml) can be -1, 0, or +1.
- The spin quantum number (ms) can be +1/2 or -1/2.
For example, the following set of quantum numbers represents a valid 3p sublevel:
n = 3l = 1 ml = 0 ms = +1/2
Orbital Shapes and Orientations, Identify the correct values for a 3p sublevel.
| Orbital | Shape | Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| 3px | Dumbbell | x-axis |
| 3py | Dumbbell | y-axis |
| 3pz | Dumbbell | z-axis |
Energy Levels and Spectroscopic Transitions
The energy level diagram of a 3p sublevel is shown below:
[Diagram energi]
The possible spectroscopic transitions involving 3p orbitals are:
- 3p → 2s
- 3p → 3s
- 3p → 3d
The wavelengths of these transitions can be calculated using the Rydberg formula:
λ = 1/R (1/n1^2
1/n2^2)
where R is the Rydberg constant (1.0973731 × 10^7 m^-1).
Applications in Chemistry
The properties of 3p sublevels influence chemical bonding and molecular interactions in several ways:
- The 3p orbitals can participate in covalent bonding by forming sigma and pi bonds.
- The 3p orbitals can also participate in coordinate covalent bonding.
- The 3p orbitals can be involved in resonance and hyperconjugation.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of the 3p sublevel?
The 3p sublevel is important because it represents a specific energy level and angular momentum state of electrons within an atom. It plays a role in determining the chemical properties and behavior of elements.
How do I determine the correct values for a 3p sublevel?
To determine the correct values for a 3p sublevel, you need to consider the quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. The principal quantum number (n) is 3, the azimuthal quantum number (l) is 1, and the magnetic quantum number (ml) can have values from -1 to 1. The spin quantum number (ms) can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
What are the shapes of the 3p orbitals?
The 3p orbitals have dumbbell shapes with two lobes separated by a nodal plane. The three 3p orbitals are oriented along the x, y, and z axes.